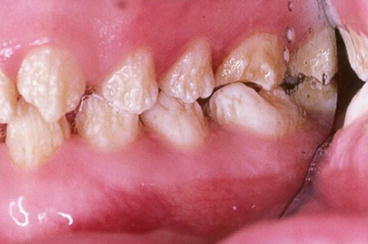
What is Amelogenesis Imperfecta?
Amelogenesis Imperfecta or AI is a rare congenital disease of the tooth. In Amelogenesis imperfecta, there will be abnormal development of the Enamel. Tooth with Amelogenesis Imperfecta will be small, yellow or brown in color and very prone to damage. The incidence of the disease varies from 1:700 to 1:1400 people depending on the geography((Crawford PJ, Aldred M, Bloch-Zupan A. Amelogenesis imperfecta. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:17.)). It is also known as Enamel dysplasia, AI, Brown Enamel or Brown Opalescent Teeth.
What causes Amelogenesis Imperfecta?
Amelogenesis imperfecta is a rare genetical disease caused by mutation of some genes. The genes are AMELX, ENAM, and MMP20 etc. These genes are responsible for creating a protein which helps in the maturation of Enamel. Due to the mutation in these genes, they fail to create that protein and tooth maturation does not take place adequately. These proteins are Enamalin, Amelogenin, Ameloblastin, Tuftelin etc.
Types of Amelogenesis Imperfecta (( Crawford PJ, Aldred M, Bloch-Zupan A. Amelogenesis imperfecta. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:17.))(( Lam E. Dental Anomalies. In: White SC, Pharooh MJ, editors. Oral Radiology: Principles and Interpretation. Elsevier: India; 2009. pp. 303–37.))(( Rajendran R. Developmental disturbances of oral and paraoral structures. In: Rajendran R, Shivapathsundharam B, editors. Shafer’s textbook of oral pathology. New Delhi, India: Elsevier; 2009. pp. 3–80))
Amelogenesis Imperfecta is classified on the basis of its clinical features, radiographic features, and appearance of Enamel.
1. Hypoplastic AI 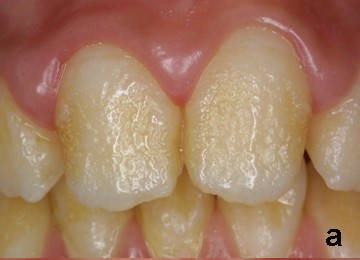
The hypoplastic form of amelogenesis imperfecta is characterized by –
- Thin enamel with yellowish-brown color, rough or smooth and glossy surface.
- Square-shaped crown lack of contact between adjacent teeth.
- Flat occlusal surfaces of the posterior teeth due to attrition, and with/without grooves and/pitting.
- Radiographically, in hypoplastic type, there is a presence of a thin radiopaque layer of enamel with normal radiodensity.
- Histologically, in hypoplastic type, the defect is in enamel matrix formation.
- Type I represents the majority of all cases of amelogenesis imperfecta.
2. Hypocalcified AI
The hypocalcified form of AI is the most common type and is characterized by-
- In this form size of the crown will be normal.
- Enamel will be softer, which wears down rapidly and can be removed by a prophylaxis instrument.
- The color of enamel will be pigmented dark brown.
- Radiographically, in hypocalcified form, the thickness of enamel is normal but radiodensity of enamel is less than that of dentin.
- Histologically, in hypocalcification type, defects of matrix structure and mineralization are seen.
- This is the least common type of amelogenesis imperfecta, representing about 7 percent of all cases.
3. Hypomaturation AI
Hypomaturation form of AI is characterized by-
-
The thickness of enamel will be normal
- Enamel will be softer than normal but harder than hypocalcified type and may crack away from the crown.
- mottled-colored cloudy white/yellow/brown/snow capped.
- Radiographically, radiodensity of enamel is similar to that of dentin.
- Histologically, in hypomaturation type, alterations in enamel rod and rod sheath structures had been noted in various studies.
- Hypomaturation represents between 20 to 40 percent of all cases of amelogenesis imperfecta.
Hypoplastic-hypomaturation with taurodontism((Amelogenesis imperfecta: a clinician’s challenge.Chamarthi V, Varma BR, Jayanthi MJ Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2012 Jan-Mar; 30(1):70-3.))
In hypoplastic-hypomaturation with taurodontism form-
- The enamel will be thin.
- Mottled yellow to brown, and pitted surface.
- Molar teeth exhibit taurodontism and other teeth have enlarged pulp chambers.
Diagnosis
AI is generally diagnosed by a dentist. The dentist will take a family history and perform the oral examination to check your enamel. Radiographs are also an important tool to check enamel from inside. Usually, the diagnosis can be made by visual examination of the tooth.
Radiographs can help the dentist to check the density of the enamel. With the help of radiographs, the dentist will determine which type of treatment you need.
Treatment
The main objectives of treatment are pain relief, preserving the patient’s remaining dentition, and to treat and preserve the patient’s occlusal vertical height.
Some examples of treatment options include:
1. Bonding
High-density dental plastic materials such as composite resins, ceramic veneers are attached to the tooth to fill the gaps. Bonding is generally used in the hypoplastic type of AI because it has enough tooth strength to hold the bonding materials.
Full crown restoration
In the hypocalcified and hypomaturation type of AI, the enamel is usually weak to hold bonding materials. For this type of AI, placement of crown over the tooth is the good option for treatment. Crown also helps in preventing tooth decay.
Orthodontic Treatment
Orthodontic treatment may also be needed in the person with AI. It is not to straighten the tooth but to create enough space for restoration.
Maintaining good oral hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene is very important in patients with AI. Gingivitis leads to improper placement or difficulty in placement of the restoration.